Atomic Mass: Molar Mass: The atomic mass is the sum of the mass of protons, neutrons, and electrons. It is the mass of a mole of a substance. It is denoted by m a. The symbol used for it is M. It has a unit of the unified mass unit (u) or the atomic mass unit (amu). G mol −1 is the standard unit for the molar mass. The atomic mass is an. Water (chemical formula: H2O) is a transparent fluid which forms the world's streams, lakes, oceans and rain, and is the major constituent of the fluids of organisms. As a chemical compound, a water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature. The atomic mass is useful in chemistry when it is paired with the mole concept: the atomic mass of an element, measured in amu, is the same as the mass in grams of one mole of an element. Thus, since the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams.
- Chemistry Notes for UPSC IAS Prelims (Part I)
- Chemistry Useful Resources
››More information on molar mass and molecular weight. In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all. Add up the mass of hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms in a mole of water by searching the atomic mass of hydrogen and oxygen on a periodic table. The mass of hydrogen is 1.008 g/mol; whereas, the mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol. Let’s compute the molar mass of water using the given details: Mass water = 2x mass hydrogen + mass oxygen.
- Selected Reading
Introduction
Around 500 BC, an Indian Philosopher Maharishi Kanad, first time postulated the concept of indivisible part of matter and named it ‘pramanu.’
In 1808, John Dalton used the term ‘atom’ and postulated the atomic theory to the study of matter.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms.
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matters, whether they are elements, compounds, or mixtures, are composed of small particles known as atoms.
Salient features of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
All matter is made of very miniscule particles known as atoms.
Atom is an indivisible particle, which cannot be created or destroyed through chemical reaction.
All atoms of an element are identical in mass and chemical properties whereas, atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
To form a compound, atoms are combined in the ratio of small whole numbers.
In a given compound, the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant.
Atomic Mass
The mass of an atom of a chemical element; it is expressed in atomic mass units (symbol is u).
The atomic mass is roughly equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons present in the atom.
One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to the exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12 and the relative atomic masses of all elements have been calculated with respect to an atom of carbon-12.

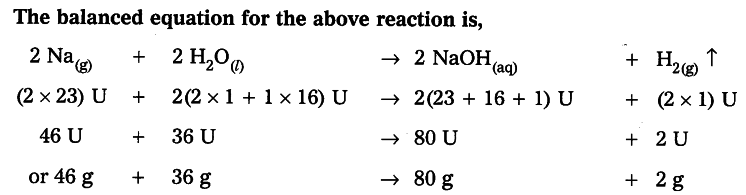
Molecule
The smallest particle of an element or a compound, which is capable to exist independently and shows all the properties of the respective substance.
A molecule, normally, is a group of two or more atoms which are chemically bonded together.
Atoms of the same element or of different elements can join (with chemical bond) together to form molecules.
Advanced file support is at the core of the back-end technology behind Affinity Designer. All the major image and vector file types are supported, including PDF/X4, EPS, SVG and PSD support. No subscription and 50% off We don’t expect you to pay us monthly either. Clipping an HSL adjustment to a specific vector object Clipping in Affinity Photo. Clipping imagery inside shapes. Clipping a Black and White adjustment to a specific image layer Clipping in Affinity Publisher. Placed content in picture frames is automatically clipped to the picture frame. Affinity photo vector. Affinity Photo The fastest, smoothest and most precise image editing software around, this essential app will revolutionise the way you work, whether you’re editing and retouching images, creating full-blown multi-layered compositions or making beautiful raster paintings. In Affinity Photo, two types of masking are possible: Pixel masking: performs a similar task to the erase tools with one important difference; a pixel mask can be modified, or even discarded, at any point in time. Vector masking: this involves using vector content as a mask over another layer that crops to the vector content's outline.
The number of atoms that constitute a molecule is known as its atomicity.
Ion
A charged particle is known as ion; it could be either negative charge or positive charge.
The positively charged ion is known as a ‘cation’.
The negatively charged ion is known as an ‘anion.’
Chemical Formulae
A chemical formula of a compound demonstrations its constituent elements and the number of atoms of each combining element.
The chemical formula of a compound is the symbolic representation of its Composition.
2.4m Followers, 3,429 Following, 3,616 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from @TonyFergusonxt (@tonyfergusonxt). The latest tweets from @tonyfergusonxt. The latest tweets from @DustinPoirier. Tony ferguson twitter. — Tony Ferguson (@TonyFergusonXT) March 31, 2021 Taunting Khabib over his supposed love of cake, Ferguson labelled the Russian a “fathead” while adding the hashtag “You’ll See Me Soon Buddy” – hinting at lingering hopes to meet Khabib in the octagon one day, despite the latter being very much retired. The latest tweets from @TonyFergusonXT.
The combining capacity of an element is known as its ‘valency.’
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is calculated by taking the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of respective substance. For example, the molecular mass of water is calculated as −
Atomic mass of hydrogen = 1u
Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 u
The water contains two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen.
Molecular Mass of Water is = 2 × 1+ 1×16 = 18 u (u is the symbol of molecular mass).
Formula Unit Mass
The formula unit mass of a substance is calculated by taking the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound.
Avogadro Constant or Avogadro Number
Avogadro was an Italian scientist who had given the concept of Avogadro Number (also known as Avogadro Constant).
The number of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) present in 1 mole of any substance is fixed, and its value always calculated as 6.022 × 1023.
In 1896, Wilhelm Ostwald had introduced the concept of ‘mole;’ however, mole unit was accepted to provide a simple way of reporting a large number in 1967.
Law of Conservation of Mass
During a chemical reaction, sum of the masses of the reactants and products remains unchanged, which is known as the ‘Law of Conservation of Mass.’
Law of Definite Proportions
In a pure chemical compound, its elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass, which is known as the ‘Law of Definite Proportions.’
Atomic Mass Of H2o
Molar mass of H2O = 18.01528 g/mol
This compound is also known as Water or Dihydrogen Monoxide.
Convert grams H2O to moles or moles H2O to grams
Molecular weight calculation:
1.00794*2 + 15.9994
| Symbol | # of Atoms | Hydrogen | H | 1.00794 | 2 | 11.190% | |
| Oxygen | O | 15.9994 | 1 | 88.810% |


In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.
The atomic weights used on this site come from NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology. We use the most common isotopes. This is how to calculate molar mass (average molecular weight), which is based on isotropically weighted averages. This is not the same as molecular mass, which is the mass of a single molecule of well-defined isotopes. For bulk stoichiometric calculations, we are usually determining molar mass, which may also be called standard atomic weight or average atomic mass.
Formula weights are especially useful in determining the relative weights of reagents and products in a chemical reaction. These relative weights computed from the chemical equation are sometimes called equation weights.
If the formula used in calculating molar mass is the molecular formula, the formula weight computed is the molecular weight. The percentage by weight of any atom or group of atoms in a compound can be computed by dividing the total weight of the atom (or group of atoms) in the formula by the formula weight and multiplying by 100.
Atomic Mass Unit Of Water
Using the chemical formula of the compound and the periodic table of elements, we can add up the atomic weights and calculate molecular weight of the substance.
Finding molar mass starts with units of grams per mole (g/mol). When calculating molecular weight of a chemical compound, it tells us how many grams are in one mole of that substance. The formula weight is simply the weight in atomic mass units of all the atoms in a given formula.
A common request on this site is to convert grams to moles. To complete this calculation, you have to know what substance you are trying to convert. The reason is that the molar mass of the substance affects the conversion. This site explains how to find molar mass.




