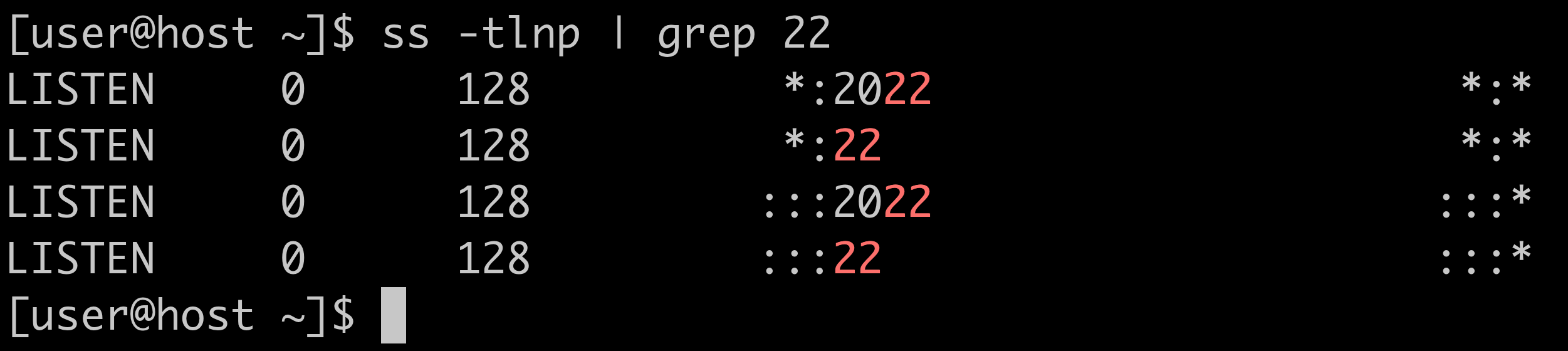
SSH is a widely used protocol for system administration and file transfer. In addition, it has a feature called SSH tunnelling (or SSH port forwarding). It creates an encrypted connection between. 2013/2/17: SSH password harvesting attacks have been reported on non-standard ports: There's No Protection In High. This port completely by modifying. Running multiple instances of sshd on RHEL5/6 is supported. Follow the steps below to configure a second instance of the sshd daemon. Make a copy of the. Since openssh-5.3p1-117.el6.x8664 for separating the ssh and sftp port on the CentOS/RHEL systems, make changes to the /etc/ssh/sshdconfig file and add the following modifications. # vi /etc/ssh/sshdconfig Port 22 Port 2222. Comment the default subsystem and add the.
| Outdated: |
| The information on this page maybe no longer relevant. |
| Note: |
| As of SME9 there is the AutoBlock feature and there is the Fail2ban contrib. |
| Note: |
| 2013/2/17: SSH password harvesting attacks have been reported on non-standard ports: There's No Protection In High Ports Anymore Do not rely solely on changing the listening port when securing ssh on your server. |
- 1Changing the default ssh port on SME 7
- 1.3Procedure: SME 7.1.3
Changing the default ssh port on SME 7
Author: mmccarn
References: sans.org article on securing ssh and Guessing passwords
Based on: Changing the default ssh port written by cc_skavenger. Use his howto if you are running SME 5.6 - 6.x!
- Update 7/25/07 to point out that this howto is not needed as of SME 7.2
- Updated 5/28/07 to correct minor typos and improve clarity
Introduction
In order to change the default port used by the sshd server in SME 7.0 you must change two configuration files on the SME server:
- you must tell sshd what port to listen on in /etc/ssh/sshd_config and
- (pre 7.1x) you must configure /etc/rc.d/init.d/masq to allow inbound traffic on your new sshd port
As of SME 7.1.3 (and possibly from 7.1 onwards?) you can change this port completely by modifying configuration database entries (there is no longer a need to create a custom template).
SME 7 uses the special db values 'TCPPort' and UDPPort' to control the iptables configuration instead of in the 'masq' templates as was done on 5.6 - 6.0x. See http://wiki.contribs.org/DB_Variables_Configuration#IPTables_firewall_.28masq.29 for more information.
This howto demonstrates
- (pre 7.1) how to use a custom template fragment to modify sshd_config
- how to change the configuration database to open the desired non-standard port for your sshd server
- how to use 'expand-template' to re-generate the new sshd_config and masq files
- how to force the sshd and firewall services to recognize the new configurations
I have inserted the procedure for SME 7.1.3 here and left the old procedure in place below for anyone still running 7.0
Procedure: SME 7.2
- Login to server-manager on your SME
- Select 'Remote access' (under 'Security')
- Enter the desired port number in 'TCP port for secure shell access'
- Click 'Save'
Procedure: SME 7.1.3
Summary Version:
(note: these commands will still work in 7.2)
See Conclusions
Annotated Version (same as 'Summary Version', but with explanations & verification)
- Check, then modify the TCPPort setting for sshd
(should return '22')
Peaks for mac. (should now return <newport>)

- Regenerate the firewall rules and sshd configuration
(this modifies the firewall rules to allow inbound traffic on <newport> and recreates /etc/ssh/sshd_config)
- Check that sshd_config was updated and restart sshd
(should return 'Port <newport>')
(restart sshd, causing it to recognize the new values in /etc/ssh/sshd_config)
Existing connections will remain unaffected, so that you *can* safely execute this procedure remotely. If you do change the sshd port remotely, be sure to open a connection on <newport> before you disconnect your existing session!
Please read the Conclusions section below for important security information. SSH should NOT be open for password access from the Internet!
Procedure: SME 7.0
- Modify the firewall and sshd settings to allow inbound traffic on the new port (only the 2nd command is required, the first and third commands are included only to allow you to verify that the database was updated properly).
(should return '22')
(where <newport> is the same port number you entered into 10Port above. There is no visible result of this command)
(should now return <newport>)
- Now expand the templates:
- Verify the results:
(should return 'Port <newport>')
(should return ' # sshd: TCPPort <newport>, AllowHosts: 0.0.0.0/0, DenyHosts:')
Download any video online for mac. While the actual port assignment comes on the next line in /etc/rc.d/init.d/masq, both lines are pulled from the configuration database - if this line looks OK, the actual invocation should look fine, too!
- Restart the services:
Sshd Listen On Multiple Ports
Be sure to test your modifications before you have to rely on them! Make sure you can connect to your server using the new port value from both inside and outside of your network.
Conclusions
This Howto was developed in response to the recommendations in this article at isc.sans.org. The article briefly suggests taking 3 steps to secure your server against ssh attacks:
- Run ssh on a non-standard port
- Choose good passphrases, and enforce them with PAM or other wrappers.
- Monitor your logs, then consciously look at blocking and/or reporting abusive netblocks.
Sshd Listen Multiple Ports

Now you know how to run ssh on a non-standard port, at least. Don't be fooled into thinking that this will bring long-term securiy, however! There is a discussion of this issue in the forums here on contribs that concludes that moving ssh to another port will only help until the attackers upgrade their tools. Public/private key security is recommended. (See Guessing passwords)
Sshd Multiple Ports




